We’re excited! This is a major release for the entire Caristix platform with significant new features.
Workgroup
New Features
- Message Comparison: compare messages one-on-one. Do a deeper form of gap analysis on content in addition to format.
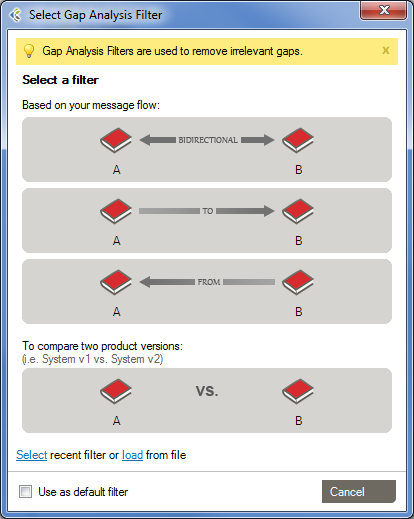
- Re-engineered Gap Analysis
- Pre-set Gap Analysis Filters to speed up gap analysis work. Set a filter based on message flow or directly compare product versions.
- Filters help you identify the gaps that matter the most, with far fewer clicks.
- Reduced noise on Usage attribute. Default to “Optional” whenever needed, for simpler Gap Analysis with only the gaps that impact the interface.
- Fuzzy Matching option: when Fuzzy Matching is on, eliminate gaps based on typos and grammar. For instance, “Smith,” would equal “Smith” (with a comma vs. without)
Coming Soon
- C-CDA add-on
- One-click updates: API add-on
- Connector for easier, more cost-effective eGate migrations
- Contact us to learn more
Enhancements
De-Identification
- Static and String generators are now merged, making them simpler to use. Add a static value directly within the string generator.
- Numeric and Decimal generators are now merged for simplicity. Just add a decimal point to a numeric to create a decimal value.
Search & Filter
- Create a data filter directly from the message definition and data distribution. This enables you to identify messages with unexpected field values, which lets you understand context in code sets.
Conformance
New Features
- Message Comparison: compare messages one-on-one. Do a deeper form of gap analysis on content in addition to format.
- Re-engineered Gap Analysis
- Pre-set Gap Analysis Filters to speed up gap analysis work. Set a filter based on message flow or directly compare product versions.
- Filters help you identify the gaps that matter the most, with far fewer clicks.
- Reduced noise on Usage attribute. Default to “Optional” whenever needed, for simpler Gap Analysis with only the gaps that impact the interface.
- Fuzzy Matching option: when Fuzzy Matching is on, eliminate gaps based on typos and grammar. For instance, “Smith,” would equal “Smith” (with a comma vs. without)
Cloak
- Static and String generators are now merged, making them simpler to use. Add a static value directly within the string generator.
- Numeric and Decimal generators are now merged for simplicity. Just add a decimal point to a numeric to create a decimal value.
Pinpoint
- Create a data filter directly from the message definition and data distribution. This enables you to identify messages with unexpected field values, which lets you understand context in code sets.



 Work in a health system or for a provider organization? This tip on healthcare data is especially important for you.
Work in a health system or for a provider organization? This tip on healthcare data is especially important for you. Tip 1: HL7 Interface Standards and 3 Challenges
Tip 1: HL7 Interface Standards and 3 Challenges