We provide an API for parsing HL7 and XML as well as the standard JSON API to transform messages in those formats into queryable objects. The API is based on the ES5 version of JavaScript and makes uses of some ES6 extension methods.
See HTTP to learn how to perform HTTP/HTTPS requests in your JavaScript code.
See NetworkConnections to learn how you can make use of the predefined connections to your integration engine or REST API in your JavaScript code.
See Profiles to learn how you can use a conformance profile in your JavaScript code.
See Snippet Manager to learn how to manage code snippets that can be re-used across your Caristix applications.
The HL7 Parser allows you to transform an HL7v2 message string into a queryable object, Message, alongside other utility methods.
The HL7.parse(`MSH|…`) returns an array of Message object.
var message = HL7.parse(`
MSH|^~\&|GHH LAB, INC.|GOOD HEALTH HOSPITAL|ADT1|GOOD HEALTH HOSPITAL|20210305104622||ACK^A01^ACK|ACK-MSG00001|T|2.5.1
MSA|AA|MSG00001`);
Returns an array of components values. An optional parameter can be used to override the default component delimiter.
var components = HL7.splitField('component 1^component 2^component 3');
log(components);
// ['component 1', 'component 2', 'component 3']
Returns an array of sub-components values. An optional parameter can be used to override the default sub-component delimiter.
var subComponents = HL7.splitComponent('sub-component 1&sub-component 2&sub-component 3');
log(subComponents);
// ['sub-component 1', 'sub-component 2', 'sub-component 3']
Returns true if the element’s value is equal to the NULL character. The NULL character is represented by transmitting “”.
var isNull = HL7.isNull('""');
log(isNull);
// true
Returns true if the element’s value is not empty.
var isPopulated = HL7.isPopulated(nonEmptyField);
log(isPopulated);
// true
Returns true if the element’s value is empty.
var isNotPopulated = HL7.isNotPopulated(nonEmptyField);
log(isNotPopulated);
// false
The Message object allows you to fetch the underlying elements (segments, fields, components, sub-components) and properties.
Get the MSH.3 – Sending Application field value
Get the MSH.5 – Receiving Application field value
Get the MSH.9.1 – Message Code and MSH.9.2 – Trigger Event (ADT_A04), or the MSH.9 – Message Type field value if MSH.9.1 or MSH.9.2 is not specified.
Returns the first segment, field, component, or sub-component object matching the given position. See the position definition.
Returns an array with all segment, field, component, or sub-component objects matching the given position. See the position definition.
Returns a string representation of the message.
The segment object allows you to fetch the underlying elements (fields, components, sub-components) of the segment.
Returns the first field, component, or sub-component object matching to the given position. See the position definition.
Returns an array with all field, component, or sub-component objects matching the given position. See the position definition.
Returns a string representation of the segment.
The Field object allows you to fetch underlying elements (components, sub-components) of the field.
Get the position of the field.
var pid_8 = message.get('PID.8');
log('Position: ' + pid_8.position);
// Position: PID.8
Get the absolute position of the field.
var pid_8 = message.get('PID.8');
log('Position: ' + pid_8.absolutePosition);
// Position: PID[1].8[1]
Returns the component or sub-component object matching the given position. See the position definition.
Returns a string representation of the field. If the field contains components or sub-components, the toString() method will include component and sub-component values and delimiters.
*Type Coercion: The field object can be converted to a string automatically (implicit conversion).
var pid_8 = message.get('PID.8');
log('Value: ' + pid_8);
log('With conversion: ' + pid_8 == 'M');
log('Without conversion: ' + pid_8 === 'M');
// Value: M
// With conversion: true
// Without conversion: false
Sets the value of the field. If the field contains components or sub-components, component and sub-component delimiters can be used to set their values.
var pid_3 = message.get('PID.3');
pid_3.setValue("1234567^4^M11^ADT01^MR^University Hospital");
log('Value: ' + pid_3);
// Value: 1234567^4^M11^ADT01^MR^University Hospital
The Component object allows you to fetch underlying sub-components of the component.
Get the position of the component.
var pid_5_2 = message.get(‘PID.5.2’);
log(‘Position: ‘ + pid_5_2.position);
// Position: PID.5.2
Get the absolute position of the component.
var pid_5_2 = message.get(‘PID.5.2’);
log(‘Position: ‘ + pid_5_2.absolutePosition);
// Position: PID[1].5[1].2
Returns the sub-component object matching the given position. See the position definition.
Returns a string representation of the component. If the component contains sub-components, the toString() will include sub-component values and delimiters.
*Type Coercion: The component object can be converted to a string automatically (implicit conversion).
var pid_5_2 = message.get('PID.5.2');
log('Value: ' + pid_5_2);
log('With conversion: ' + pid_5_2 == 'John');
log('Without conversion: ' + pid_5_2 === 'John');
// Value: John
// With conversion: true
// Without conversion: false
Sets the value of the component. If the component contains sub-components, sub-component delimiter can be used to set their values.
var pid_5_1 = message.get('PID.5.1');
pid_5_1.setValue("Beethoven&van");
log('Value: ' + pid_5_1);
// Value: Beethoven&van
The SubComponent object allows you to get its value.
Get the position of the sub-component.
var pid_5_1_1 = message.get('PID.5.1.1');
log('Position: ' + pid_5_1_1.position);
// Position: PID.5.1.1
Get the absolute position of the component.
var pid_5_1_1 = message.get('PID.5.1.1');
log('Position: ' + pid_5_1_1.absolutePosition);
// Position: PID[1].5[1].1.1
Returns a string value of the sub-component.
*Type Coercion: The sub-component object can be converted to a string automatically (implicit conversion).
var pid_5_1_1 = message.get('PID.5.1.1');
log('Value: ' + pid_5_1_1);
log('With conversion: ' + pid_5_1_1 == 'Doe');
log('Without conversion: ' + pid_5_1_1 === 'Doe');
// Value: Doe
// With conversion: true
// Without conversion: false
Sets the value of the sub-component.
var pid_5_1_1 = message.get('PID.5.1.1');
pid_5_1_1.setValue("Beethoven");
log('Value: ' + pid_5_1_1);
// Value: Beethoven
The position is a string that allows you to target one or many elements inside a message. The position should be expressed using the following structure:
segment-id[segment-repetition*].field-position[field-repetition*].component-position.sub-component-position
(*those fields are optional, they indicate if the user is targeting a single element. If not specified, every element inside the message corresponding to the position will be targeted)
Here are some examples:
Segment:
MSH||||||
OBX||||||
OBX||||||
OBX||||||
MSH||||||
OBX||||||
OBX||||||
OBX||||||
Field:
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
OBX|||||OBX.5~OBX.5|
Component:
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1^OBX.5.2|
Sub-Component:
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
MSH||||||
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
OBX|||||OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2~OBX.5.1.1&OBX.5.1.2^OBX.5.2|
The HTTP Module allows you to create HTTP and HTTPS requests as HTTPRequest objects, send them, and use their responses as HTTPResult objects.
The HTTP module exposes methods for creating HTTPRequest objects.
Creates an HTTPRequest from the provided HTTP request method and resource URI.
var request = HTTP.create('GET', 'https://daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4/Patient');
Creates an HTTPRequest from the provided HTTP request method, NetworkConnection object and resource URL path. Request host, client certificate and timeout are obtained from the NetworkConnection.
var connection = NetworkConnections.getConnection('DaaS Caristix FHIR R4 Server');
var requestFromConnection = HTTP.createFromNetworkConnection('GET', connection, '/Patient');
This object exposes properties and methods to edit and send an HTTP request.
The HTTP method used by the request, as defined when creating the request.
var method = request.method;
// The value should be equal to "GET".
The fully-qualified URI of the request, as defined when creating the request.
var uri = request.uri;
//The value should be equal to "https://daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4/Patient"
Sends the request and returns the result.
var result = request.send();
Sets the request’s body to the provided string.
request.setBody('MSH|^~\&|');
//The request's body should be equal to "MSH|^~\&|"
Sets the request’s timeout in seconds to the provided amount. The default value is 30 seconds.
request.setTimeout(5);
//The request's timeout should be equal to 5 seconds.
Sets the request’s Client Certificate using the provided serial number.
request.setCertificate('7571563212351');
Adds an HTTP header to the request.
request.setHeader('accept', 'application/json');
//The request should contain the "Accept" header with value "application/json"
This object exposes properties to read an HTTP response’s body and status code.
The response’s body.
var body = result.body;
The response’s HTTP status code.
var status = result.statusCode;
var succeeded = status == 200;
The NetworkConnections module allows you to access the Network Connections found in the Network Connections menu, as seen below. The Network Connections can be accessed as NetworkConnection objects.

Default Network Connections as configured in the Default Connections menu can also be accessed.
The NetworkConnections module exposes method for obtaining NetworkConnection objects, including the default Network Connections.
Returns the Network Connection that has the provided name.
var connection = NetworkConnections.getConnection('DaaS Caristix FHIR R4 Server');
// Should return the Network Connection with the name "DaaS Caristix FHIR Server R4 Server"
// and the host "daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4"
Returns the default HL7 Receive Network Connection.
var sendConnection = NetworkConnections.getDefaultReceiveHL7Connection();
// Should return the Network Connection with the name "Caristix Field Mapping Channel"
// and the host "daas.caristix.com"
Returns the default HL7 Send Network Connection.
var ReceiveConnection = NetworkConnections.getDefaultSendHL7Connection();
// Should return the Network Connection with the name "Caristix Field Mapping Channel"
// and the host "daas.caristix.com"
Returns the default HL7 Send Network Connection.
var webServiceConnection = NetworkConnections.getDefaultWebServiceConnection();
// Should return the Network Connection with the name "DaaS Caristix FHIR Server R4 Server"
// and the host "daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4"
The NetworkConnection object allows you to read all the Network Connection properties that you can access from within the Network Connections menu, as well as a method for obtaining the fully-qualified URL of the Network Connection.
The Network Connection’s Name property.
var name = connection.name
// name should be "Daas Caristix FHIR R4 Server"
The Network Connection’s Host property.
var host = connection.host
// host should be "daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4"
The Network Connection’s Port property.
var port = connection.port;
// port should be 443
The Network Connection’s default Timeout property.
var timeout = connection.timeout;
// timeout should be 30
The Network Connection’s Client Certificate serial number.
var certificate = connection.certificate
Returns the Network Connection’s fully-qualified URL, including protocol, host and port.
If the protocol is not included in the Host property, the protocol is either https (if the port is 443) or http (if using any other port).
The default ports for serving content over HTTP and HTTPS, 80 and 443 respectively, are excluded from the URL.
var url = connection.getUrl()";
// url should be "https://daas.caristix.com/fhir_r4"
The Profiles module allows you to access your Caristix Library’s conformance profiles. The conformance profiles can be accessed as Profile objects.
The Profiles module exposes methods for obtaining Profile objects.
Returns the Profile that matches the provided path in the Caristix Library.
var profile = Profiles.getProfile('HL7Reference/HL7 v2.5.1.cxp');
// Should return the HL7v2.5.1 Profile from the library
Returns the reference profile set in the application’s options.
var referenceProfile = Profiles.getReferenceProfile();
The Profile object allows you to fetch data from a conformance profile.
Returns a table object if the table exists, otherwise it returns null.
var administrativeSexTable= profile.getTable('0001');
// Should return the 0001 - Administrative Sex table
The Table object allows you to access the properties about a given table in a conformance profile, as well as access its entries.
The name of the table.
var tableName = administrativeSexTable.name;
// tableName should be "Administrative Sex"
An array containing all of the table’s entries.
var entries = administrativeSexTable.values;
// entries should be the table entries corresponding to the values A, F, M, etc.
Returns true if the given value exists in the table’s entries. This method is case-sensitive.
var containsM = administrativeSexTable.contains('M');
// Should return true
Returns the first entry which matches the provided value. If none are found, returns null.
var maleEntry = administrativeSexTable.get('M');
// Should return the M TableEntry
The TableEntry object allows you to access the details of a table’s entry.
The display name of the table entry.
var maleLabel = maleEntry.label;
// maleLabel should be "Male"
The Value of the table entry.
var maleValue = maleEntry.value;
// maleValue should be "M"
Returns the given custom-column property value.
var deprecated = maleEntry.getExtraContentValue('DEPRECATED');
// Should return false
Returns the string value of a table entry.
var stringValue = maleEntry.toString();
// Should return "M"
The snippet manager allows you to write, test and save scripts for future use. To access it, go into any textbox in which the JavaScript API can be used, right-click the textbox and select “Insert Code Snippet…”

From there, you can select one of the scripts you’ve written, or one of the default Caristix Samples.
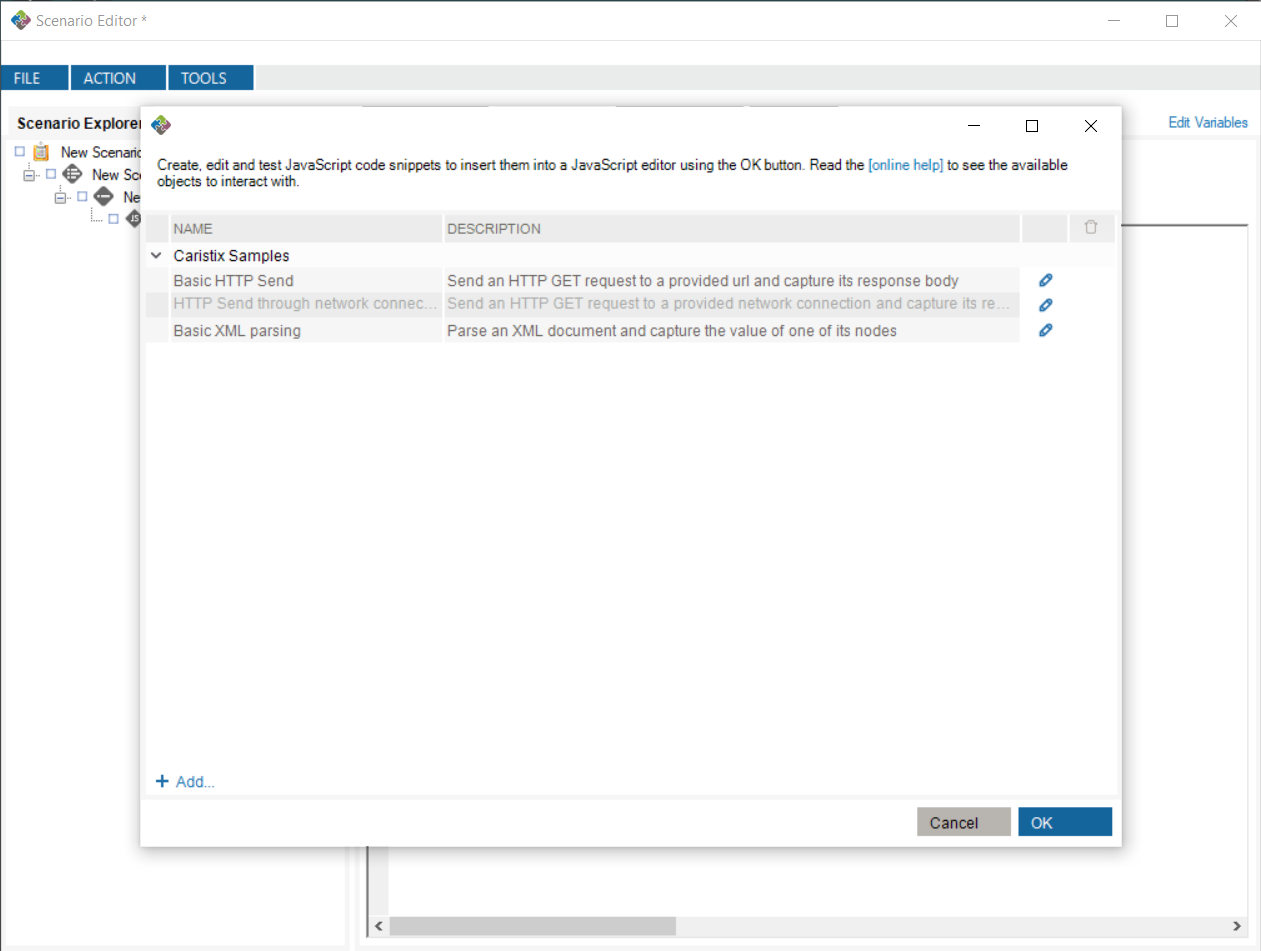
Clicking “OK” after selecting a script inserts that script at the position of the caret in your JavaScript editor.
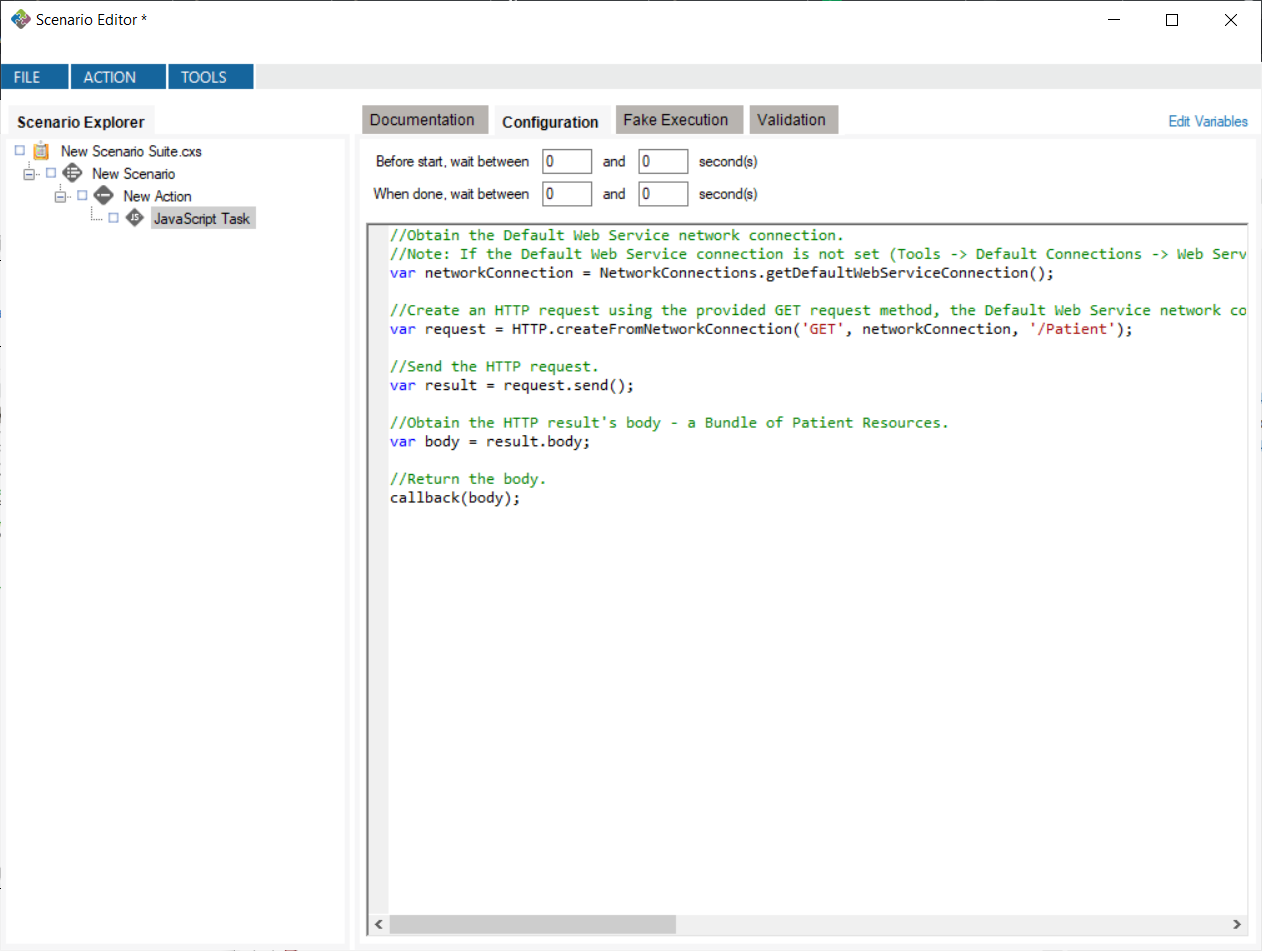
You can create your own code snippets by clicking the “+ Add…” button. You can edit the snippet by clicking the edit  button, opening the JavaScript editor window. Once the window is closed, any changes you make will automatically be saved. Note: any changes to Caristix Samples will not be saved.
button, opening the JavaScript editor window. Once the window is closed, any changes you make will automatically be saved. Note: any changes to Caristix Samples will not be saved.
The JavaScript editor window contains fields for editing, naming, describing, grouping and testing your snippets.
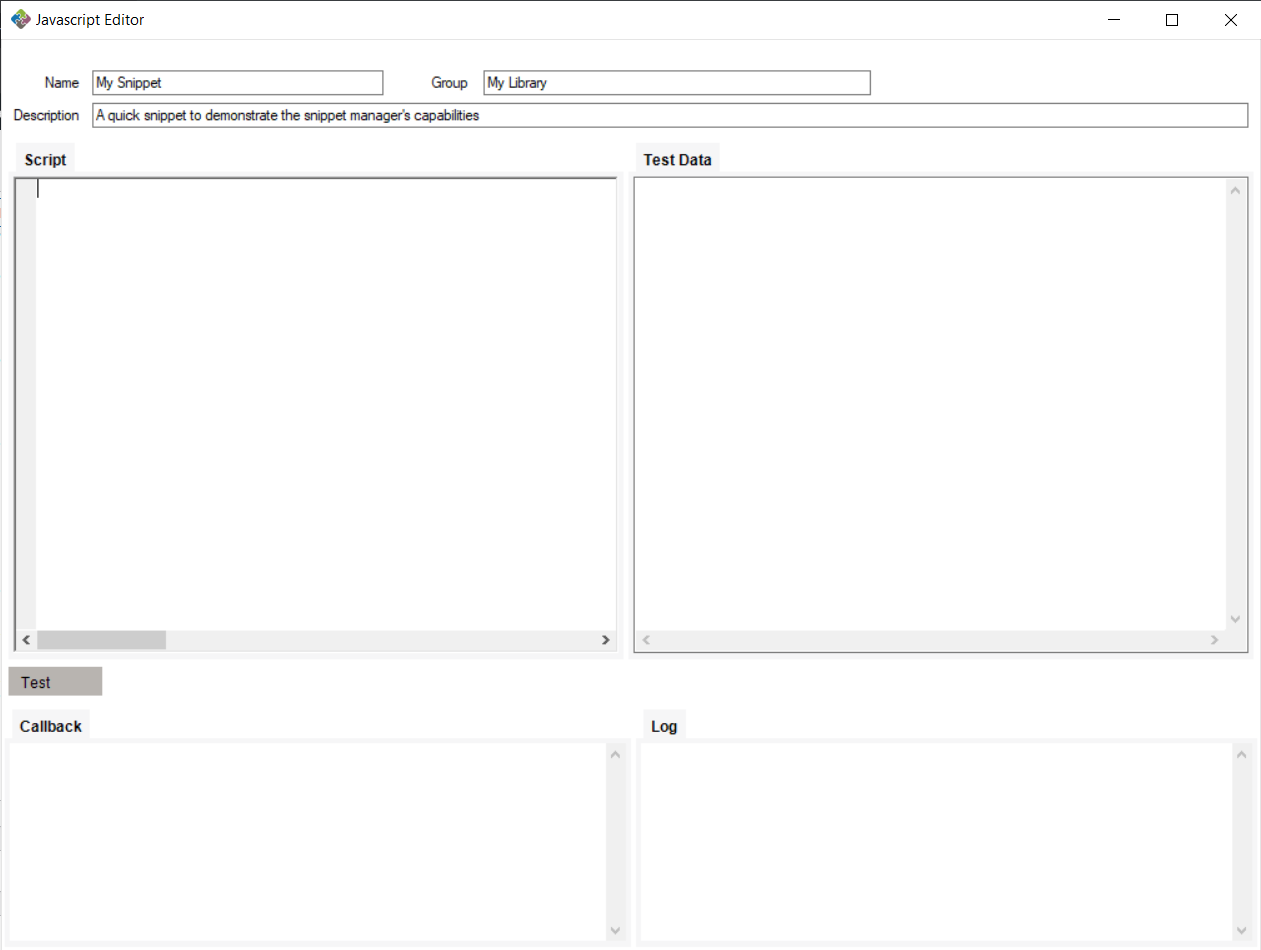
Using the same group name for different snippets causes them to be grouped together in the snippet manager.

While writing your snippet, you can test it by feeding it text. Writing data such as HL7 messages in the Test Data field places that in the JavaScript editor’s context as the testData property. This property can be accessed in your snippet while testing. Note: outside of testing snippets, the testData property will always be null.

By clicking the “Test” button, you can test using the data you provide in the Test Data field. Callback and log information gets shown in the Callback and Log textboxes.

The XML Parser allows you to transform an XML-string into a queryable object, XPathNavigator.
var xmlObj = XML.parse('<xml><element attribute="value1" /><element attribute="value2" /></xml>');
This object exposes properties and methods to query an XML element easily using X-Path.
https://www.w3schools.com/xml/xpath_syntax.asp
The XML object’s value. If the object is an element, the value is the text inside between start and end tags or the inner XML content if applicable. If the object is an attribute, the value is the attribute’s value.
var firstElement = xmlObj.selectFirst('/xml/element/@attribute');
var value = firstElement.value;
// The value should be equal to "value1".
Returns the first occurrence of the provided X-Path, or undefined if there are no occurrences.
var element = xmlObj.selectFirst('/xml/element');
// Should return the first <element> inside the <xml> node.
Returns an array with all occurrences of the provided X-Path, or an empty array if no occurrences.
var elements = xmlObj.select('/xml/element');
// Should return an array with all <element> inside the <xml> node.
Returns a string representation of the XML element.
var element = xmlObj.selectFirst('/xml/element');
var value = element.toString()
// The value should be equal to "<element attribute="value1" />".